8 Sales Forecasting Methods: A Definitive Guide

Contents
How many leads do we need to generate to hit goals? Do we need to hire more sales reps to boost our revenue? How much revenue will this new product generate? These are all important questions that sales forecasting methods can help your company answer.
Sales forecasting is pivotal to a company’s success and helps business executives make smart decisions when it comes to setting sales goals, hiring, launching new products and budgeting for the upcoming quarter or year.
In this guide we cover best practices of sales forecasting and eight different methods, along with the pros and cons of each.
- Chapters
- 01 What Is Sales Forecasting?
- 02 Why Is Sales Forecasting Important?
- 03 8 Sales Forecasting Methods
- 04 Sales Forecasting Best Practices
- 05 Common Sales Forecasting Mistakes
- 06 FAQs
- 07 CRM Systems for Sales Forecasting
What Is Sales Forecasting?
Sales forecasting is a data-informed process that predicts how much revenue a company will make in a given time period — e.g., a weekly, monthly, quarterly or yearly basis depending on the needs of the company.
Sales forecasting takes into account various factors such as historical data, economic and industry trends and a company’s existing sales pipeline. Essentially, the goal of a sales forecast is to address these questions: How much money will a company make? And when is that revenue expected to come in?
Sales forecasts can help companies make strategic plans; however, they’re not rock-solid projections. Just like weather forecasts, sales forecasts are not 100% accurate and can be under or overestimated, so it’s important to understand that they fluctuate based on markets, economic trends and company changes like layoffs or hiring.
Why Is Sales Forecasting Important?
Sales forecasts are all about helping companies strategically plan for the future by determining:
- Internal budgets: Sales forecasting helps make sure teams and companies at large stay within their budget for the quarter/year.
- Growth rates: Having a sense of where your company is headed makes it easier to hit your sales quota and even surpass those goals.
- Supply chain purchasing and preparation: Being able to project sales numbers and understand how seasonality affects them can help your business properly purchase inventory.
- Hiring and capacity planning: High periods of sales means you might need a larger staff; down periods might mean layoffs. Sales forecasting can help you plan accordingly.
- Sales and partner strategies: Sales forecasting adds value across a company, helping you internally prepare for sales and properly strategize with partnerships.
For private companies, sales forecasting helps employees and leaders gain trust and confidence in their business. On the other hand, sales forecasting helps publicly traded companies gain credibility in the market.
8 Sales Forecasting Methods
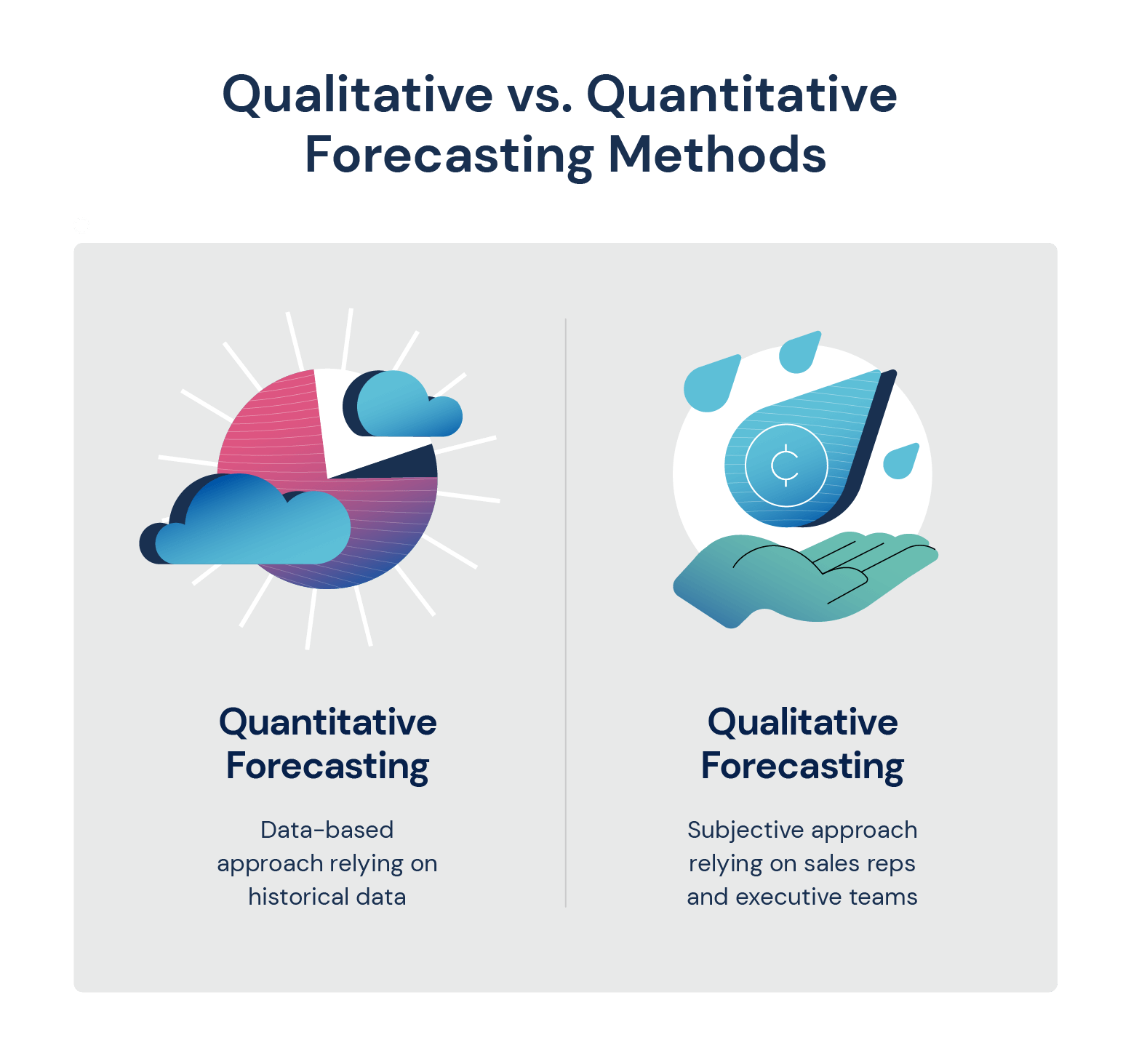
While there are a number of different forecasting methods, most will fall under two umbrella categories: quantitative and qualitative.
- Quantitative Forecasts: These forecasts take a data-based approach to sales forecasting, relying on historical data of past sales revenue to help predict future trends. Quantitative forecasts can take both a bottom-up and top-down approach. Bottom-up approaches compare a specific period to the same period the year before and suggest increases in growth based on that comparison. Top-down quantitative approaches take into account market information and other various factors to determine a forecast.
- Qualitative Forecasts: These forecasts are more subjective in nature and rely on the opinions of sales reps, executive teams and other market variables to forecast sales revenue. Qualitative forecasting is typically the simplest forecasting method for a company to execute, however, it also comes with a degree of error since it’s highly subjective.
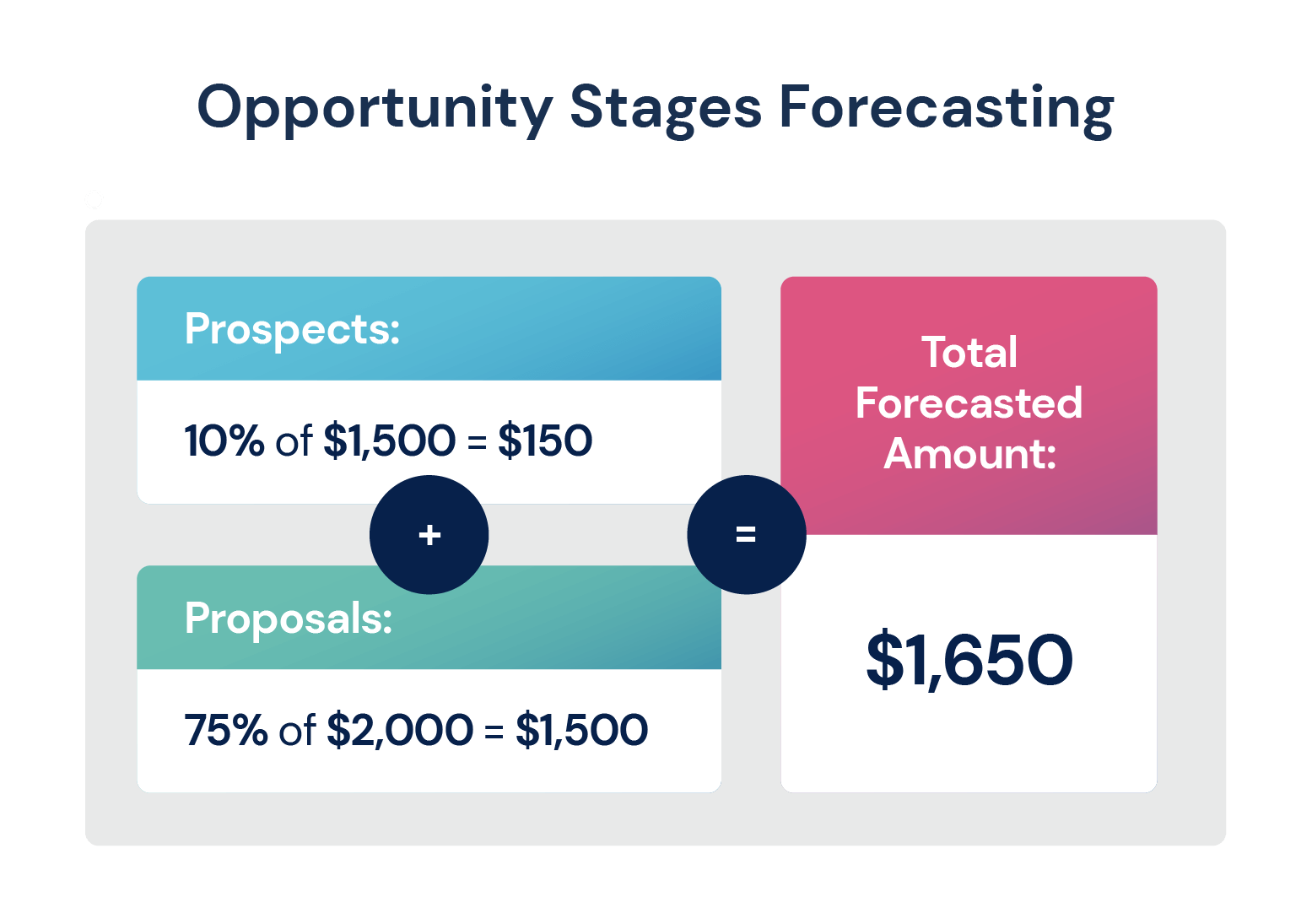
Opportunity Stages Forecasting
Opportunity stages forecasting is based on the chance of closing future deals or sales that you have lined up in your pipeline.
Most businesses break their sales pipeline into the following stages:
- Prospects
- Qualified
- Proposals
- Closing
- Wins/losses
Let’s say you have $1,500 in prospects typically close 10% of them, then you have $2,000 at the proposal stage which you’d typically close ¾ of your sales for, then your total opportunity stages forecasting suggests you have a total of $1,650 in deals for that given time period.
Pros
- Easy to use
- Can be paired with CRM programs
Cons
- Doesn’t take into account the subjectivity of sales deals
- Not accurate without input from sales reps
Length of Sales Cycle Forecasting
Length of sales forecasting assesses sales based on the age of the deal.
To calculate with this method, use the total number of days it took to close any recent deals, then divide that by the total number of closed deals.
 For example, let’s say your company closed six recent deals:
For example, let’s say your company closed six recent deals:
- Deal 1: 60 days
- Deal 2: 65 days
- Deal 3: 44 days
- Deal 4: 52 days
- Deal 5: 31 days
- Deal 6: 49 days
You would then divide the total number of days (301) by six for an average of 50 days. Given this time frame, no matter how promising a deal might seem or how many deals you have in your pipeline, you’d still forecast any deals you have to close in roughly two months.
Pros
- Simple forecasting method
- Uses objective data
Cons
- Doesn’t take into account the nuances of individual deals
- Requires very accurate tracking of the sales cycle which can be tedious
Historical Data Forecasting
Also referred to as time series forecasting, historical data forecasting is a method that analyzes past data to predict your business’s sales based on the same period of the previous year. This method will often assume a growth rate from the past period.
For example, if you had $60,000 in sales last September and assume a 10% growth rate, then you’d forecast $66,000 for this September.
Pros
- Simple method that’s easy to implement
- Accurate so long as the market doesn’t experience significant changes
Cons
- Doesn’t account for seasonality or changes in the market
- Doesn’t take into account demands from changing environments
Linear Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is an in depth, quantitative forecasting method that requires a solid understanding of statistics and the different elements that impact your company’s sales. At the most basic level, it involves looking at the different variables that influence sales and calculates the relationships between them.
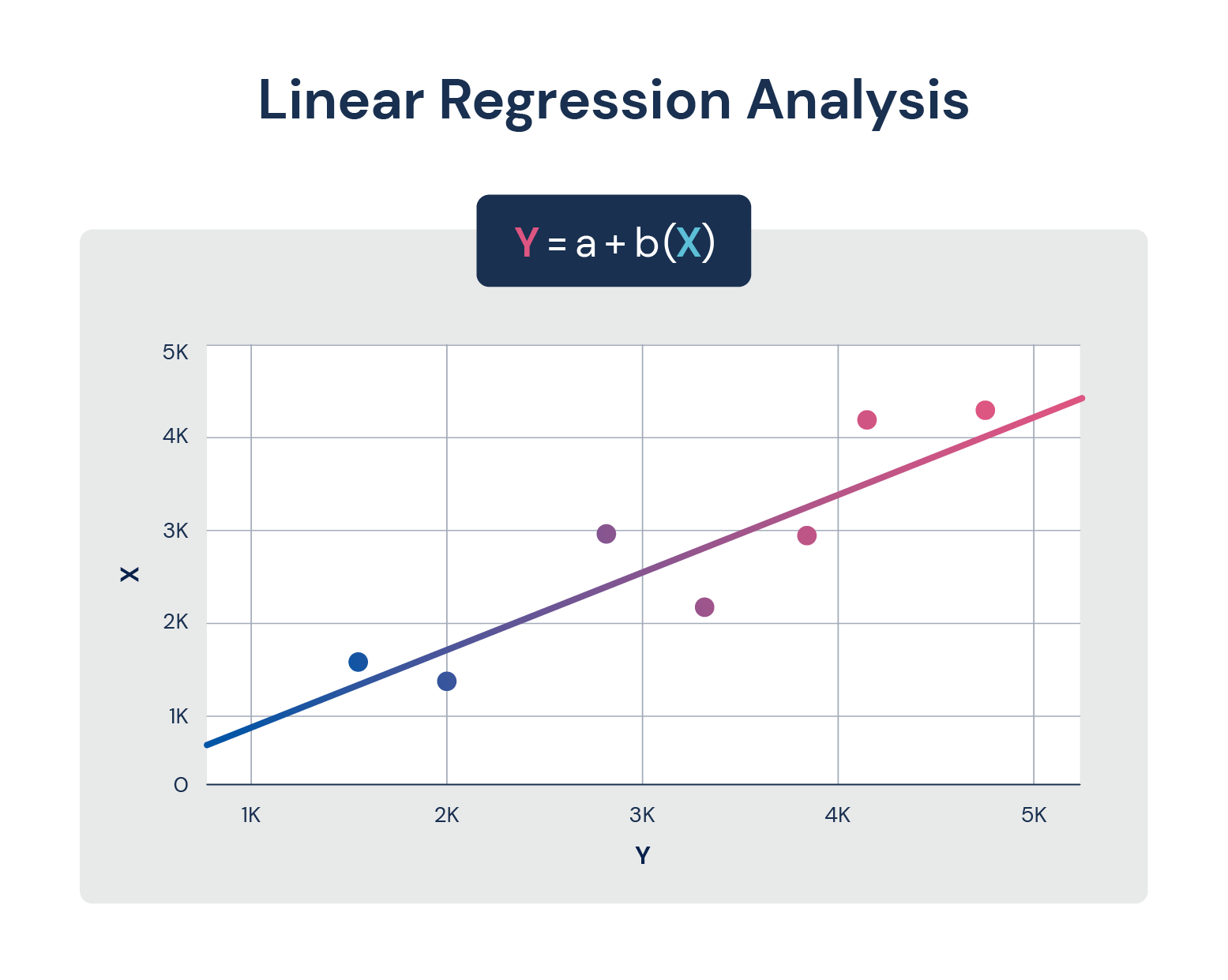
Regression analysis uses the formula Y = a + bX. To run a regression analysis, you must first:
- Determine why you’re forecasting and what you want to learn from it.
- Determine the most affected factor — this could be sales, for example, which you’d label as your Y (or the dependent variable in the equation).
- Identify independent variables (X in the equation) that might be affecting your sales.
- Narrow down a time period.
- Collect the data for both your dependent (Y) and independent (X) variables.
- Choose a software, like Excel, to run your regression model.
- Analyze a correlation between your X and Y variables.
For example, if you want to forecast sales for the upcoming year and how to hire sales reps accordingly, you could look at the relationship betweens sales calls (your X variable) and sales (your Y variable) between the past five years. 
Using the regression analysis formula, your equation would be Sales = a + b(sales calls), which you’d plot on a graph accordingly using a regression analysis software. Keep in mind that the a and b in the equation will be calculated automatically by the software. The software will help you generate a line of best fit showing how closely related the relationship between sales and sales calls was over your chosen time periods. Based on this data, you can then determine if you need to hire more sales reps for the upcoming year.
Pros
- Good for companies looking to fine-tune their forecasting strategy
- Good for enterprises because of objectivity
- Gives a realistic view of a company’s forecast numbers
Cons
- Difficult to run and comprehend
- Requires solid knowledge of statistics
Pipeline Forecasting
Pipeline forecasting analyzes each opportunity or potential sale sitting in your company’s sales pipeline and predicts its success to close based on a variety of factors like age, deal type and deal stage. It’s a very accurate and sophisticated method but relies on heavy amounts of data and custom tools, which may not be accessible for every company.
Pros
- Accounts for each step of the sales pipeline
- Data centric and accurate
Cons
- Needs custom tools to account for different sales factors
- Requires heavy amounts of data
Intuitive (Sales Rep) Forecasting
Intuitive forecasting is a method that relies on the opinion of sales reps on how confident they are that a deal in their pipeline will close. Because sales reps are the closest to their sales prospects and the products or services they’re selling, they tend to have the best insight.
However, intuitive forecasting is also very subjective, as sales reps tend to be optimistic and could give overly generous answers. Because intuitive forecasting doesn’t rely on sales data like many of the other methods discussed above, it only works if you have candid sales reps who you can trust.
Pros
- Easy to implement
- Sales reps have the best insight on products they sell
Cons
- Highly subjective method
- Sales reps tend to give overly optimistic insights
Scenario Writing
Scenario writing is a forecasting method that focuses on possible extremes based on a specific set of assumptions. With this method, forecasters will draft several different cases for deals in a pipeline and conclude the best- and worst-case scenarios.
Most scenario writing follows an eight-step process:
- Focal issues: yearly sales
- Key factors: factors influencing yearly sales, such as sales calls, demos and product inquiries
- External forces: competition or government restrictions
- Critical uncertainties: any challenges that might arise over the next year, such as a new technology that customers gravitate toward, which reduces sales
- Scenarios: consider every possible scenario
- Scenario logics: consider each scenario’s possible end and what will happen next
- Implications and options: your next steps based on the different scenario options
- Early indicators: consider how these relate to focal issues and key factors to help with planning
Pros
- Effective method when each possible outcome around uncertainties have a developed action plan
Cons
- Relies on a subjective understanding of business and sales
- Time-consuming
Multivariable Forecasting
Multivariable forecasting is what the name suggests — it incorporates different factors from the methods above like length of a sales cycle, opportunity forecasting, sales rep input and historical data. Forecasting based on multiple variables is generally the most accurate, but it’s also the most complex and requires an advanced analytics solution, which is best implemented by large-scale organizations with the budget to do so.
Pros
- Leans on multiple factors, making it the most accurate
- Good for large-scale organizations
Cons
- Complex and requires customs systems
- Not recommended for startups or small businesses
Sales Forecasting Best Practices
As you can see, there are many methods for forecasting sales. Regardless of which method your company uses, there are always some best practices to be followed:
- Establish a clear sales process
- Use accurate data
- Lean on historical data
- Incorporate changes
- Anticipate market trends
- Analyze the competition
- Lean on collaborative input from different departments
It’s best to look at sales forecasting as something to build upon. Always aim to take learnings from previous forecasts to refine future forecasting methods. By using more advanced forecasting processes and tools and building upon previous forecasts, companies can outperform their competitors because they’ll have a deeper understanding of what drives their business and how to shape the outcome of a sales period before that period comes to a close.
Common Sales Forecasting Mistakes
Of course, producing consistently accurate sales forecasts is not without its challenges. Some common pitfalls that you want to be aware of include inaccurate data, inefficiency and total subjectivity.
Inaccurate data
While usually unintentional, inaccuracy is one of the biggest pitfalls of sales forecasting and can lead to mistrust amongst teams and stakeholders. There are a number of reasons why data in a sales forecast might be inaccurate, such as:
- Poor adoption and training of CRM software throughout the company
- Data inconsistency across teams or incomplete data from sales reps
- Inconsistency with the methods stakeholders use to produce the forecasts
- A lack of collaboration across different departments and teams
Inefficiency
Inefficiencies are especially common when working with large sales forecasts and with large teams or across departments. In these cases, a forecast will often have multiple owners, which can leave more room for errors. Additionally, if a team is not aligned on the rules of the forecast, then there can be disputes and errors in how it’s produced, which can lead to multiple revisions.
Subjectivity
While many forecasting methods are data driven, all rely somewhat on the forecaster making good decisions on how the data is used. Because highly data-driven methods tend to be more complex and time-consuming, many companies rely on easier, more subjective methods like opportunity stages and intuitive forecasting.
FAQs
Which Method Is Best for Sales Forecasting?
Which forecasting method is best will often be determined by your company’s needs, size and budget. However, data-driven forecasting methods are typically the most accurate. Multivariable forecasting in particular is the most accurate forecasting method out there.
What Is a Sales Forecast Example?
Most sales forecasting methods will fall under the umbrella of quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative sales forecasts are subjective and rely on either sales teams or executive teams to make projections. Quantitative methods take a data-based approach to sales forecasts and tend to be more time and resource intensive for teams.
A simple example of a quantitative method is the length of sales cycle forecast, which takes the total number of days it took to close any recent deals and divides that by the total number of closed deals.
Who’s Responsible for Sales Forecasting?
Sales leaders are almost always responsible for sales forecasting. In most cases, the VP of sales will be the one orchestrating the forecasting report.
CRM Systems for Sales Forecasting
Investing in a customer relationship management (CRM) system is an important part of giving your sales department accurate data to work with.
Even if you’re a startup and are just getting off the ground, having a CRM in place and ensuring your sales reps know how to use it will streamline work down the road when you put together your sales forecast.
When it comes to automating sales prospecting, tools like Mailshake can help your sales teams send out significantly more emails while still keeping personalization top of mind. Mailshake can also help support your sales forecasting by providing you with accurate sales prospecting data.





